Description
Selling Bromadol Hcl (BDPC)
Selling Bromadol Hcl (BDPC)
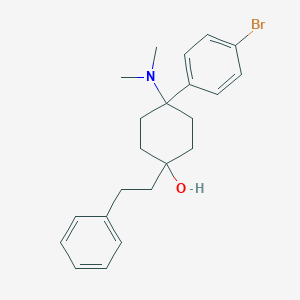
Selling Bromadol Hcl (BDPC). BDPC (systematic name 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-phenylethyl)cyclohexanol; also known as bromadol) is a potent fully synthetic opioid with a distinctive arylcyclohexylamine chemical structure. It was developed by Daniel Lednicer at Upjohn in the 1970s.[1] Initial studies estimated that it was around 10,000 times the potency of morphine in animal models.[2] However, later studies using more modern techniques assigned a value of 504 times the potency of morphine for the more active trans-isomer.[3] This drug was first seized along with three kilograms of acetylfentanyl in an April 25, 2013 police action in Montreal, Canada,[4] and has reportedly continued to be available on the designer drug market internationally.[5][6] Analogues where the para-bromine is replaced by chlorine or a methyl group retain similar activity, while the meta-hydroxyl derivative demonstrated robust antagonist activity
Bromadol
Bromadol is an analytical reference material categorized as an opioid. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
<br< p=””></br<>
Scientific Research Applications
- Identification and Quantitative Analysis in Bromadol : A study by Li, Huang, Guo, and Zhuang (2014) identified 2-phenylethanol as a major impurity in commercial this compound samples. They established a new HPLC quantitative analysis method for this impurity, finding it constituted 9.6% by weight. They also devised a method to remove this impurity from this compound, which could facilitate mass production (Li, Huang, Guo, & Zhuang, 2014).
- Toxicity and Bioaccumulation in Earthworms : Liu et al. (2015) explored the toxicity and bioaccumulation of bromadiolone, a rodenticide, in earthworms. They found significant inhibition of earthworm growth and changes in antioxidant activities, suggesting a risk to earthworms and potentially the wider ecosystem from bromadiolone bait applications (Liu, Xiong, Ye, Zhang, Yang, & Ji, 2015).
- Impact on Wildlife and Sustainable Management of Rodents : Coeurdassier et al. (2014) discussed the high level of wildlife poisoning following treatments of fields with bromadiolone in Europe. They emphasized the need for more sustainable management of rodent outbreaks, proposing practices like direct control of voles at low density and landscape management (Coeurdassier, Riols, Decors, Mionnet, David, Quintaine, Truchetet, Scheifler, & Giraudoux, 2014).
- Effect on Mus musculus : A study by Revathi and Yogananda (2006) showed that bromadiolone had significant effects on the blood, liver, and kidneys of Mus musculus (house mice) at various time intervals, highlighting its toxicological impact (Revathi & Yogananda, 2006).
Safety and Hazards
Future Directions
Bromadol has been reported to be available on the designer drug market internationally . Controlling analogues of this compound in future drug control legislation may be an effective and pre-emptive response and may halt the diversification of such analogues entering the market currently and in future .
Mechanism of Action
Mode of Action
Opioids typically work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking pain signals and inducing a feeling of euphoria .
Result of Action
Bromadol is reported to have a potency around 504 times that of morphine for the more active trans-isomer . This suggests that it has a strong analgesic effect, providing significant pain relief.
Biochemical Analysis
Biochemical Properties
Bromadol HCL BDPC is a potent opioid receptor agonist
Cellular Effects
The cellular effects of this compound HCL BDPC are primarily due to its action as an opioid receptor agonist It can influence cell function, including impacts on cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism
Molecular Mechanism
This compound HCL BDPC exerts its effects at the molecular level primarily through its action as an opioid receptor agonist It may involve binding interactions with biomolecules, enzyme inhibition or activation, and changes in gene expression
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
This compound HCL BDPC has been found to be a highly potent analgesic in animal models
Properties
IUPAC Name |
4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-phenylethyl)cyclohexan-1-ol | |
|---|---|---|
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H28BrNO/c1-24(2)22(19-8-10-20(23)11-9-19)16-14-21(25,15-17-22)13-12-18-6-4-3-5-7-18/h3-11,25H,12-17H2,1-2H3 | |
InChI Key |
PRSUTWWKYIVBEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)C1(CCC(CC1)(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Br | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H28BrNO | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID201018410 | |
Molecular Weight |
402.4 g/mol | |
CAS No. |
77239-98-6 |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.